PAE と NPAE について知る前に、まずタイの財務報告基準について知りましょう。 タイには、国際財務報告基準を参照するタイ財務報告基準 (TFRS) があります。 (国際財務報告基準 – IFRS) が国際的に受け入れられるようになります。 これらの財務報告基準は、会計義務を負う法人に適用されます。 紀元前 2543 年の会計法によると、株式が証券取引所で取引されている上場企業であるかどうか または証券取引所外の一般法人ですが、国際財務報告基準が適用される場合 に使用することを目的とした 公益団体 (Publicly Accountable Entities-PAE) と複雑です。 財務報告書作成の基礎として公正価値(Fair Value)の概念を使用することから。 これは負担であり、財務報告書の作成にコストがかかります。 公益性のない団体 (非公的責任主体 – NPAE)、そのほとんどは中小企業です。
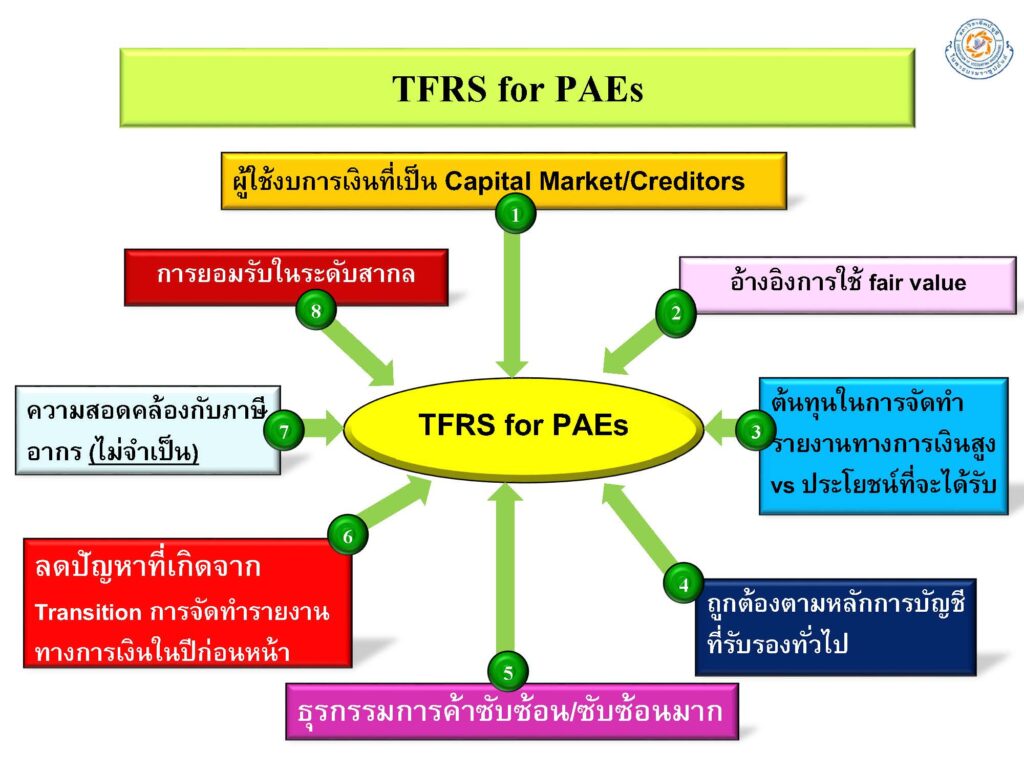
Publicly Accountable Entities | PAEs
公開会社(Publicly Accountable Entities:PAEs)」とは、以下の特徴を持つ企業を指します
- 公開会社(Publicly Accountable Entities:PAEs)は、公開市場で株式または債券を取引する企業を指します
- 納品を行っている、または納品中の事業者 証券取引委員会への財務諸表 タイ証券取引所 (SEC) または規制当局 有価証券の発行だけを他人に任せてください。 公開市場では、証券業務を行い、金融機関などの幅広い第三者グループの資産を管理する会社です。 生命保険会社、損害保険会社、投資信託会社 そして製品市場 タイの農業の進歩
- 公開会社
- 以下から構成される会計基準セット (TFRS (2009)) を使用して追加されるその他の事業: 32 の TAS フレームワーク、4 つの TFRS、4 つの TIC、および 1 つの TFRIC
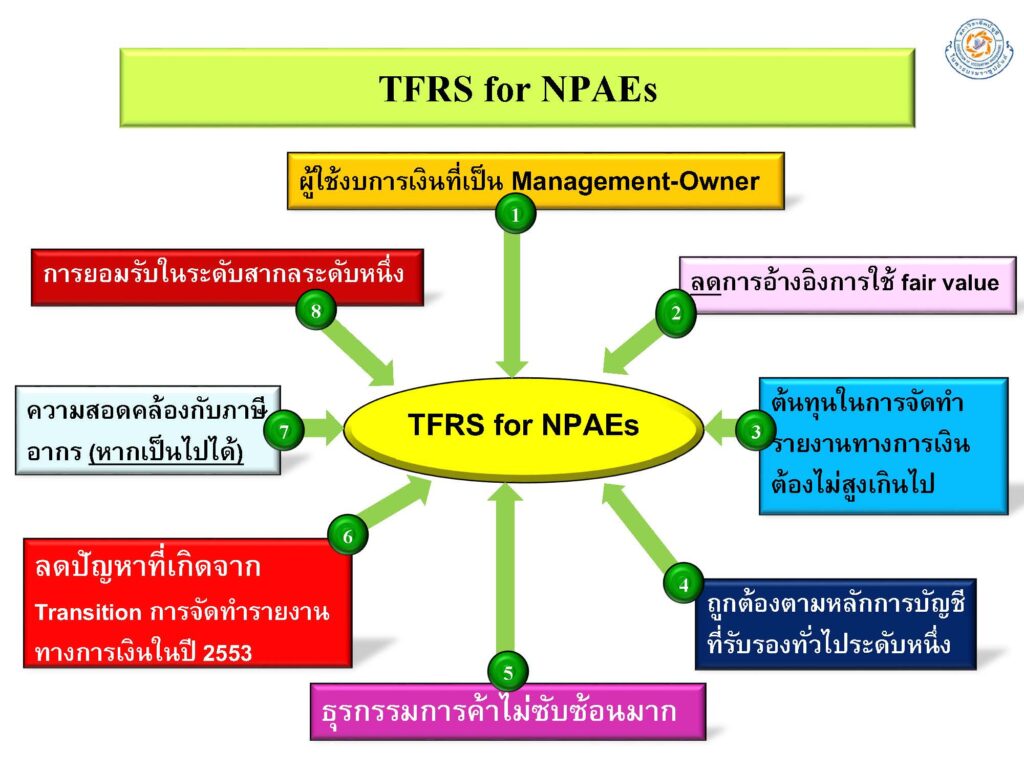
Non-Publicly Accountable Entities | NPAEs
(非公的責任主体 – NPAE) とは、小規模な会計基準セット (NPAE 用の TFRS (2011)) または大規模な会計基準セットを使用して会計処理を行っている PAE ではない企業を意味します。 NPAE に対して TFRS を設定したくない場合。
「TFRS PAEs」と「NPAEs」の基準の違いは以下の通りです
PAEs | NPAEs | |
Financial Statements | – Comprehensive Income Statement | – Profit and Loss Statement (P&L) |
– Cash Flow Statement | – statement of comprehensive income (non-disclosure of specific expenses). | |
– statement of financial position (3-period balance sheet) | ||
–income statement (mandatory disclosure of significant expenses and additional disclosure of expenses by nature). | ||
Investment capital | – cost of sales | – cost deducted by provision for depreciation |
–fair value (trading/securities held for sale). | – fair value adjustments through profit or loss and other comprehensive income. | |
Investment in subsidiaries. | – Financial statements must be prepared and recognition of profit/loss must be in accordance with the revenue and expense recognition principles. | –No need to prepare consolidated financial statements and record cost prices. |
Employee benefits. | – Calculation must be based on actuarial mathematics standards. | – Calculate using an estimation method, which the Auditor deems reasonable. |
Intangible Assets | – No need for disposal (similar to depreciation calculation), by examining whether there is impairment at the end of the year or not. | – Disposal after 10 years. |
Recognize revenue. | – According to TFRS 15’s 5-step process. | – Recognize revenue when control is transferred or at a point where risks and rewards are transferred and revenue is recognized. |
Income from real estate sales | – Revenue is recognized upon transfer. | – Can choose 3 Options |
1. Receiving income upon transfer | ||
2. Understanding income based on the proportion of successfully completed work | ||
3. Understanding income based on installment payments transferred when due | ||
Income TAX | –Calculating deferred tax assets due to differences between accounting and tax, which may result in assets/liabilities, income tax, or deferred tax assets (DTA)/deferred tax liabilities (DTL). | – No need to calculate, just record the accrued Income TAX. |