Managing an organization’s accounting system is critically important for effective business and financial management. In this article, we will explore and explain the most crucial components of the accounting system: General Ledger (GL), Accounts Payable (AP), and Accounts Receivable (AR). These are essential parts of an organization’s accounting system used to record and track financial movements and transactions in detail, ensuring the organization’s stability and accurate financial data at all times. We will delve into each account thoroughly to understand their functions and significance within the organization’s accounting system.
General Ledger (GL)
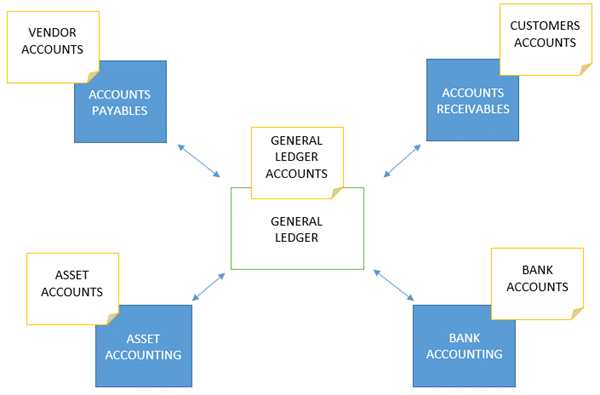
General Ledger (GL) is a financial journal or recording system used to document the details of every financial transaction that occurs within an organization. It encompasses all accounts used in the accounting system, including both financial and non-financial accounts within the organization. For each financial transaction that occurs, essential information is recorded in the GL, such as the transaction date, transaction description, amount involved, and the relevant accounts.
GL is utilized to summarize the financial status of the organization, providing insights into the organization’s profits and losses, total expenses, and the status of other financial resources of the organization.
The Importance of General Ledger (GL) Accounting
General Ledger (GL) Accounting: The Heart of Organizational Accounting Systems.
The General Ledger (GL) stands as the nucleus of an organization’s accounting framework, aggregating all financial transaction data, including various types of account journals. Recording and scrutinizing information within the GL aid in analyzing the financial status of the organization, such as profits and losses, expenditures, and the state of financial resources. Thus, it serves as a pivotal tool for financial decision-making.
Recording and Managing Data in GL:
1. Data Recording: Precise and systematic data recording in the GL is crucial. This includes specifying dates, account numbers, transaction descriptions, and amounts.
2. Verification and Adjustment: Regular verification and adjustment of data within the GL are imperative to ensure accuracy and reliability.
3. Reporting: Generating financial reports from the GL data is a vital tool for financial decision-making. The system should be user-friendly and streamlined for effective financial analysis and decision-making.
A meticulously maintained GL not only facilitates an accurate representation of an organization’s financial health but also provides essential insights for strategic financial decisions.
Accounts Payable (AP)
Accounts Payable (AP) is the account used to record payment transactions within an organization, primarily for goods or services received and pending payment. In the AP account, details of the company or individuals to be paid, payment due dates, and the amount to be paid are specified.
Managing AP is crucial as it helps maintain the organization’s credibility in paying vendors or service providers. It also saves time for the organization in verifying and settling debts within the specified deadlines.
The Importance of Accounts Payable (AP)
Accounts Payable (AP) is the account used to record payment transactions within an organization, often representing amounts owed to companies or individuals for services rendered or goods received. Efficient AP management enables the organization to pay its dues on time, reduces the risk of incurring various penalties, and helps maintain credibility in the market.
Recording and managing data in AP :
General Steps in Recording and Managing Data in Accounts Payable (AP)
Invoice Receipt:
- Receive invoices from vendors or service providers.
- Verify the accuracy of invoice details, such as product or service prices, quantities, and vendor information.
Data Entry:
- Enter invoice data into the AP accounting system.
- Specify transaction details, including item codes, amounts, and payment due dates.
Approval Workflow:
- Manage the approval process for invoices, requiring authorization from designated personnel, such as accounting managers or executives.
Payment:
- After approval, schedule payments based on the invoice due dates.
- Process fund transfers or issue checks to vendors or service providers.
Payment Recording:
- Record payment details in the accounting system, including payment reference numbers for tracking and reporting purposes.
Reconciliation and Control:
- Verify the accuracy of AP entries and ensure payment aligns with the budget.
- Reconcile accounts to maintain financial accuracy and control.
Reporting:
- Generate reports on payments, outstanding balances, and payment statuses for management and the accounting team.
Record Keeping:
- Retain relevant documents related to AP transactions for the specified legal duration according to regulations.
Accounts Receivable (AR)
Accounts Receivable (AR) is the account used to record payment transactions that an organization is awaiting from customers or buyers. In the AR account, details of customers or buyers with pending payments, payment due dates, and the outstanding amounts are specified.
Managing AR is crucial as it helps maintain the credibility of customers and aids in the organization’s financial planning. Additionally, it assists in tracking and collecting payments from customers within the specified deadlines.
Importance of Accounts Receivable (AR)
Accounts Receivable (AR) is the account used to record pending payment transactions from customers or buyers. Proper AR management ensures timely receipt of payments, reduces the risk of non-payment, and fosters customer satisfaction.
Recording and Managing Data in AR:
Invoice Generation:
- Generate invoices based on the products or services provided to customers.
- Specify details such as price, quantity, payment due dates, and customer information.
Data Entry:
- Enter invoice data into the AR accounting system, including transaction specifics like item codes, amounts, and payment due dates.
Invoice Delivery:
- Send invoices to customers using electronic methods or postal services.
Payment Verification:
- Verify customer payments upon the due date.
- Record received payments in the AR system.
Aging Analysis:
- Analyze the aging of outstanding payments from customers.
- Generate aging reports to track and identify overdue payments.
Customer Communication:
- In case of delayed or outstanding payments, contact customers to request payment and handle collection requests.
Record Keeping:
- Maintain records related to payments, including invoices and payment receipts, within the system.
Reporting:
- Generate reports on received payments, outstanding balances, and customer account statuses for management and the accounting team.